The laminin-511 E8 fragment can be used as a coating material on a substrate for culturing
pluripotent stem cells, such as iPS cells and ES cells, as well as other cell types such as
epidermal cells and nerve cells. In cell culture, the fragment, diluted in a solvent such as PBS,
can be coated onto a culture substrate. Furthermore, as described later, even if the laminin-511 E8
is not coated on the culture substrate, pluripotent stem cells can be cultured while maintaining
their undifferentiated state by simply suspending them with the cells during seeding and pouring
them onto the culture substrate. Figure 3 shows images of epidermal cells and vascular endothelial
cells cultured on iMatrix-511. Epidermal cells hardly adhere on uncoated plates, but many cells
adhere and spread on iMatrix-511-coated plates. Vascular endothelial cells adhere even on uncoated
dishes, but many are observed to remain in a rounded shape without spreading. On the other hand,
when cultured on iMatrix-511, most cells spread well.
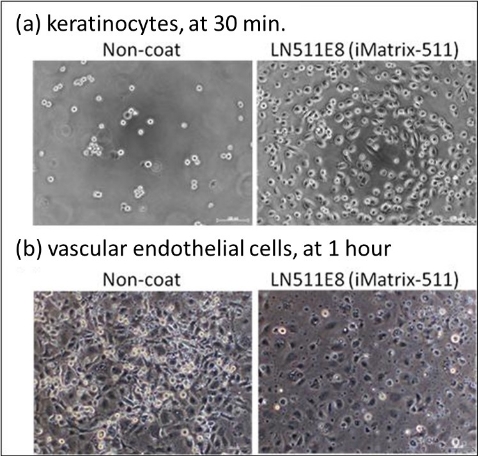
Figure 3. Adhesion and spreading of human skin epidermal cells and vascular endothelial cells
cultured on iMatrix-511
More than a decade ago, it was known that pluripotent stem cells, such as iPS cells and ES cells,
were extremely difficult to handle. For example, in order to increase the number of cells while
maintaining their pluripotency, it was necessary to passage the proliferated cell mass by dividing
it into appropriate sizes, but if the division operation was not appropriate, the pluripotency could
be lost. In addition, mouse-derived feeder cells and mouse tumor-derived basement membrane extracts
had been used as culture substrates for these cells, but due to the risk of contamination with
foreign components, this was considered to be one of the problems in medical applications. Joint
research by researchers at Osaka University and Kyoto University revealed that the laminin-511 E8
fragment is effective for culturing iPS cells and ES cells (References 6-7). Nippi manufactures this
product under license for this patent. On the laminin-511 E8 fragment, even if iPS cell masses are
broken up into individual cells, many of them can be maintained and efficiently proliferated. In
addition to laminin-511, Nippi also manufactures and sells the E8 regions of laminin isoforms 111,
221, 332, and 411. The integrin proteins expressed on the cell membrane differ depending on the
organ and tissue from which the cells are derived. By using the laminin isoform corresponding to the
integrin, appropriate signals are sent to the cells during cell culture. It has been shown that the
laminin-511 E8 fragment can maintain undifferentiated properties even if it is seeded on the
substrate together with the cells, without coating the culture substrate (Reference 8).
|